NPT Fittings
Reliable NPT Fittings for Plumbing, Gas, and Hydraulic Systems – Engineered for high-pressure, leak-proof performance, Evergood NPT fittings deliver unmatched durability and secure connections in even the toughest environments. Ideal for water, gas, oil, and chemical lines, they offer effortless installation and long-term reliability.
What Are NPT Fittings
NPT (National Pipe Tapered) fittings are essential components for creating secure, leak-proof connections in hydraulic systems. Their unique tapered design achieves a robust mechanical seal through interference fit, making them the preferred choice for manufacturing, automotive, agriculture, and construction industries worldwide.
| Feature | Technical Description |
|---|---|
| Superior Sealing | The tapered threads naturally compress during engagement. When paired with PTFE tape or sealant to fill microscopic gaps, they ensure a 100% leak-free connection by eliminating spiral leak paths. |
| High-Pressure Resilience | Specifically engineered for rigorous environments, these fittings offer exceptional resistance to vibration and thermal cycling, ensuring long-term stability in heavy-duty working systems. |
| Material Versatility | Available in Stainless Steel, Carbon Steel, and Brass to meet diverse industrial requirements for corrosion resistance, temperature extremes, and specific pressure ratings. |
| Universal Compatibility | Fully compliant with ANSI/ASME standards, these fittings provide reliable, standardized interfacing for applications ranging from high-pressure power units to low-flow fluid transfer. |
NPT Thread Chart
Dash sizes are indexed to specific thread geometries featuring a 60° tapered profile.
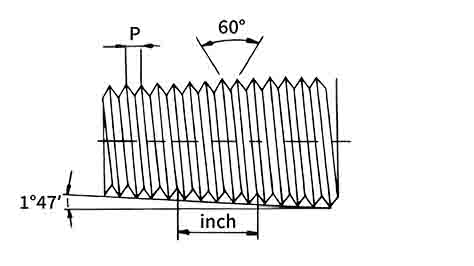
| Inch Size | Dash Size | Threads per Inch | Male Thread O.D. (in) | Male Thread O.D. | Female Thread O.D. (in) | Female Thread O.D. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 | -2 | 27 | 13/32 | 0.41 | 3/8 | 0.38 |
| 1/4 | -4 | 18 | 17/32 | 0.54 | 1/2 | 0.49 |
| 3/8 | -6 | 18 | 11/16 | 0.68 | 5/8 | 0.63 |
| 1/2 | -8 | 14 | 27/32 | 0.84 | 25/32 | 0.77 |
| 3/4 | -12 | 14 | 1 1/16 | 1.05 | 1 | 0.98 |
| 1 | -16 | 11 1/2 | 1 5/16 | 1.32 | 1 1/4 | 1.24 |
| 1 1/4 | -20 | 11 1/2 | 1 21/32 | 1.66 | 1 19/32 | 1.58 |
| 1 1/2 | -24 | 11 1/2 | 1 29/32 | 1.90 | 1 13/16 | 1.82 |
| 2 | -32 | 11 1/2 | 2 3/8 | 2.38 | 2 5/16 | 2.30 |
FAQ
Are NPT and JIC the Same?
NPT and JIC fittings are designed to address different engineering needs, each with a unique sealing mechanism:
NPT Fittings (National Pipe Thread): Primarily used in a wide range of general piping applications, including water, gas, oil, hydraulic,and chemicals, NPT fittings feature tapered threads that create a tight seal as the threads engage and compress against each other. This design is especially effective for low to high-pressure environments, providing a reliable mechanical seal to prevent leakage across various fluid types.
JIC Fittings (Joint Industry Council): Specifically designed for hydraulic systems, such as those found in construction equipment and industrial machinery, JIC fittings employ straight threads combined with a 37° flared metal seat to achieve a secure seal. This design is optimized for high-pressure fluid systems, capable of withstanding pressures exceeding 10,000 PSI. The flared seat ensures that the connection can handle the demands of high-power hydraulic circuits while maintaining integrity under extreme pressure conditions.
Are NPT and NPTF the same?
| Key Differences | NPT | NPTF |
|---|---|---|
| Sealing Mechanism | Requires sealant (e.g., Teflon tape or pipe dope) to fill gaps and create a seal. | Seals through thread deformation (interference fit), eliminating the need for sealant in most cases. |
| Thread Design | Features standard tolerances with deeper roots and a typical crest/root design. | Has tighter tolerances, shallower roots, and a unique crest/root design that forces interference for metal-to-metal sealing. |
| Applications | Commonly used for general fluid and gas lines with low and high pressure. | Preferred for more higher pressure, higher temperature, or fuel applications where sealant contamination is a concern. |
| Standards | Defined by ANSI B1.20.1. | Defined by ANSI B1.20.3. |


feedback Report comment