This air hose buying guide explores essential pneumatic hose materials (Poly, Rubber,Hybrid, PVC), diameters, and...
Hydraulic Hose Learning Tutorials From Design to Application
What Is a Hydraulic Hose ?---An Overview of Introduction
Hydraulic hoses play an important role In the world of machinery and heavy industry. The force that drives motion is often unseen. This power is the pressurized fluid, and its transmission is made possible by a crucial yet often underestimated component: the hydraulic hose. Far more than a simple tube, a hydraulic hose is a precisely engineered conduit designed to channel immense energy while withstanding extreme physical stress. Its layered construction is a testament to cutting-edge material science, ensuring reliability and safety in the most demanding operating environments.
The Science of Hydraulic Hose Layered Construction
In The functionality of a hydraulic hose is built from the inside out, beginning with its core. The innermost layer, the inner tube, is made of a special synthetic rubber chosen for its chemical compatibility with various hydraulic fluids, including mineral and synthetic oils. This layer's primary role is to prevent fluid contamination and leakage, making it the first line of defense for the entire hydraulic system.
Encircling the inner tube is the reinforcement layer, the true powerhouse of hydraulic hose. This layer is responsible for containing the ultra-high pressures that surge through the system. Manufacturers use high-tensile steel wire, synthetic fibers, or robust textiles, wrapped in precise braided or spiral patterns to build this strength. Braided hydraulic hose offers excellent flexibility, while spiral-wrapped hydraulic hose provides superior burst pressure resistance, allowing it to excel in different performance ranges.
Finally, a durable outer cover protects the entire assembly. This layer is engineered to be a barrier against external threats, including abrasion, UV radiation, ozone, and corrosive chemicals. The integrity of this outer layer is critical for the hydraulic hose's lifespan and durability, shielding its internal components from the daily wear and tear of operation.
Where are hydraulic hoses used?
From Factory to Application Site: The Versatility of Hydraulic Hoses
The remarkable adaptability of the hydraulic hose allows it to serve as a universal power link across a wide range of industries. It is what transfers fluid power from a stationary pump to a moving component, a key function that makes modern machinery so dynamic.
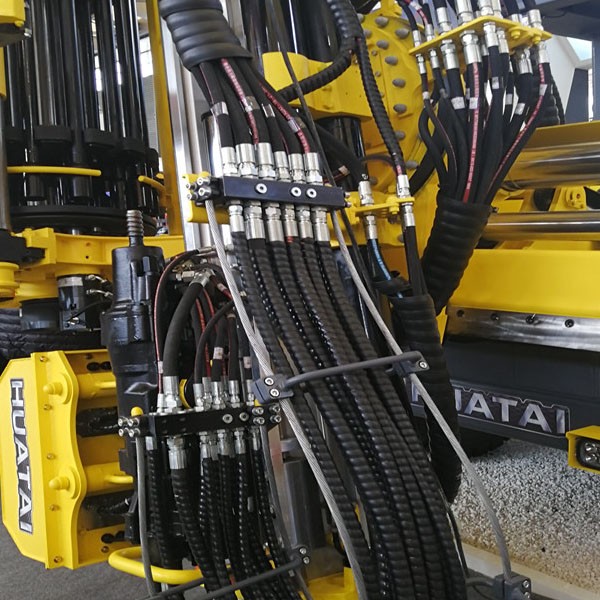
Construction, Mining, and Oil Fields: Hydraulic Hose-A Lifeline in Harsh Environments
In heavy industries like construction, mining, and oil fields, the hydraulic hose is the lifeline for heavy machinery such as excavators, bulldozers, mining drills, and drilling rigs. In these applications, the hose must endure relentless pressure spikes, such as the sudden impact generated when an excavator bucket hits hard ground, or the ultra-high pressures from mud pumps and hydraulic fracturing operations during drilling. Simultaneously, they must resist continuous external abrasion from rocks and debris on rugged terrain and withstand exposure to gas and coal dust in underground environments.
A high-quality hydraulic hose is a critical component for ensuring the reliability of deep mining equipment, directly impacting production efficiency and worker safety. In underground coal mines, hoses must not only have high pressure and abrasion resistance but also flame-retardant and anti-static properties to ensure safety in flammable and explosive atmospheres.
Hydraulic Hose in Oil Field Drilling Applications:
In oil and gas drilling, the hydraulic hose is used in the following core equipment:
- High-Pressure Mud Pumps: Used to pump mud into the wellbore, they must withstand extremely high pressures, often thousands of PSI. The hydraulic hose must resist high pressure, high temperatures, and chemical exposure from the mud.
- Hydraulic Top Drive: This is a modern drilling device, and the hydraulic hose provides power for the rotation and lifting of the drill pipe. Here, the hose must withstand continuous pressure cycling and vertical tensile forces.
- BOP Control Systems: The blowout preventer (BOP) is a critical safety device used to seal the wellbore in the event of a blowout. The hydraulic hose that controls the BOP must ensure absolute reliability under extreme pressure and harsh conditions to prevent catastrophic accidents.
- Hydraulic Fracturing Operations: In unconventional oil and gas extraction, a hydraulic hose is used for high-pressure pumping of fracturing fluid to fracture rock formations and release oil and gas. These hydraulic hose components must withstand instantaneous ultra-high-pressure shocks and high flow rates, making their material and construction crucial.
Hydraulic Hose in Underground Coal Mining Applications:
The underground environment of coal mines is challenging, with high humidity, flammable gas, and coal dust posing special requirements for the hydraulic hose. The hydraulic hose is widely used in:
- Hydraulic Supports: This is one of the most important pieces of equipment in coal mining, used to support the roof of the tunnel and ensure the safety of the working face. Hydraulic supports contain a large number of hydraulic hose assemblies that must withstand continuous high pressure and crushing from overhead rock, while also possessing excellent flame-retardant properties to prevent gas ignition.
- Shearers: Shearers rely on hydraulic systems to drive the cutting drum and travel mechanism. The hydraulic hose used here must be flexible and wear-resistant to adapt to the complex underground tunnels and frequent movements.
- Roadheaders: During the tunneling process in coal mines, roadheaders use a hydraulic hose to power the cutting head. The hydraulic hose here not only needs high-pressure resistance but also the ability to withstand impact and friction from the tunneling process and good anti-static properties to prevent static electricity from causing accidents.
Agriculture: Hydraulic Hose Fueling Modern Farming
Agricultural machinery such as combine harvesters, planters, and balers rely on the precise control provided by a hydraulic hose. The hydraulic system is responsible for adjusting cutting heights, controlling planting depth, and even driving the baling motion. In these applications, the hydraulic hose not only endures operating pressure but also handles severe natural conditions, including prolonged sun exposure, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to pesticides and fertilizers. Thus, a hose's weather resistance and chemical corrosion resistance are of utmost importance.
Industrial Manufacturing: The Pulse of Automated Production
In the manufacturing and industrial sectors, a hydraulic hose acts as the "pulse" of automated production lines. In injection molding machines, it provides high pressure to inject molten plastic; in stamping presses, it transfers immense force to shape metal parts. These applications demand high performance from the hydraulic hose, requiring it to withstand frequent pressure cycling and ensure the precision and repeatability of movements to maintain the production line's efficiency and product quality.
How to Select A Hydraulic Hose?
When purchasing a hydraulic hose, international standards are important references that provide uniform specifications for the hose's performance, dimensions, and quality.
- SAE Standards: The SAE (Society of Automotive Engineers) standard is one of the most widely used hydraulic hose standards globally, especially in North America. Common series like SAE 100R1, SAE 100R2, and SAE 100R16 detail technical parameters such as the hose's inner diameter, working pressure, burst pressure, minimum bend radius, and fluid compatibility.
- EN Standards: EN (European Norm) standards dominate the European market, such as EN 853 and EN 856. These standards are similar in performance to SAE but may differ in certain dimensions and testing methods. For example, EN 856 details specifications for spiral-reinforced hydraulic hoses used in high-pressure and ultra-high-pressure applications.
- ISO Standards: The ISO (International Organization for Standardization) standard aims for global uniformity, such as ISO 18752. This standard breaks away from traditional hose classifications and categorizes hoses based on their pressure rating and performance, providing users with a more intuitive basis for selection.
After selecting the standard, application is guided by the "STAMP" principle (Size, Temperature, Application, Media, Pressure), is crucial:
Size
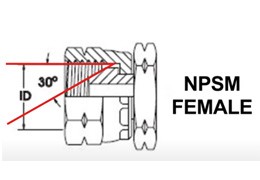
Inner Diameter (ID): This is one of the most critical parameters, as it impacts fluid flow rate and system efficiency. An ID that is too small can lead to excessive flow speed, generating turbulence, heat, and pressure loss, thereby shortening the hydraulic hose's lifespan. Conversely, an ID that is too large can reduce efficiency and increase costs. You need to calculate the most suitable ID based on your system's flow rate (GPM or LPM).
Length: The length of the hose must be precisely calculated to accommodate the full range of motion of the system. A hose that is too short will create tensile stress when the equipment extends, while one that is too long can easily get tangled, abraded, or pinched. The optimal length should allow for enough slack to accommodate all movements.
Bend Radius: Each hydraulic hose has a minimum bend radius. Bending the hose below this radius can damage the reinforcement layer, leading to premature failure. During routing, it's essential to ensure that the bend radius is greater than the manufacturer's specified minimum. Also, avoid bending the hose directly at the fitting.
Temperature
Fluid Temperature: Ensure the hose can withstand the fluid's temperature during both operation and non-operation. For example, during hot weather or high-intensity work, the fluid temperature may exceed its normal range, and the hose must be able to handle this fluctuation.
Ambient Temperature: The hose's outer cover must also be able to withstand the temperature of the external environment, whether it's a frigid outdoor setting or a hot engine compartment. Prolonged exposure to temperatures outside the limits can accelerate material degradation.
Internal and External Heat Sources: Besides the fluid itself, you must also consider other heat sources, such as engines or exhaust systems. If the hose will be routed near these sources, additional protective measures or a higher temperature-rated hydraulic hose should be chosen.
Application
Operating Environment: Carefully evaluate the external threats the hose will face. This includes external abrasion (e.g., from dragging on the ground or rubbing against equipment parts), UV radiation (prolonged outdoor use), ozone, salt water, or corrosive chemicals. Choose an outer cover with corresponding resistance to wear, weather, or chemical corrosion based on these threats.
Type and Frequency of Motion: Differentiate between hoses for static connections and those for dynamic applications. In dynamic applications, such as robotic arms or moving platforms, the hose will frequently bend and twist, requiring excellent flexibility and fatigue resistance.
Pressure Pulses and Vibration: If the hose is connected to a hydraulic hammer, crusher, or high-frequency cycling equipment, it will endure significant pressure pulses. When selecting this type of hydraulic hose, it's crucial to pay special attention to its pulse rating, which is typically determined by the hose's reinforcement layer structure (e.g., spiral wrap).
Media
Fluid Type: The inner tube must be completely compatible with the fluid being conveyed. Besides common hydraulic oils, you must also consider special media such as water-based fluids, biodegradable liquids, chemical solvents, or gases. Incompatible materials can cause the inner tube to swell, harden, or dissolve, which can contaminate the system and lead to catastrophic failure.
Fluid Cleanliness: The cleanliness of the media is critical for the lifespan of a hydraulic hose. Fluid containing impurities can abrade the inner tube like sandpaper at high flow rates. Therefore, choosing a hose with a smooth inner wall and ensuring the system has effective filtration is key.
Pressure
- Working Pressure: This is the maximum pressure the hydraulic hose should be able to continuously withstand during normal system operation. For safety, the hose's rated working pressure should be at least equal to or higher than the system's maximum working pressure.
- Pressure Peaks: Many systems experience brief pressure spikes during startup, directional changes, or load shifts, which can be much higher than the rated working pressure. The hydraulic hose must be able to withstand these peaks to prevent instantaneous rupture.
- Burst Pressure: This is the highest pressure the hose can theoretically withstand, typically four times the working pressure. This safety factor is a key indicator of the hose's durability and reliability.
Where to buy hydraulic hose?
Using the above criteria, you can determine what hydraulic hose is and how to choose the right model. Then, you can go to your local hydraulic store to purchase it. For bulk purchases, I recommend Evergood.
Choosing a reliable hydraulic hose supplier is just as important as selecting the hose itself. At Evergood Hose Factory, we implement rigorous quality control for our hydraulic hose from start to finish, which is our core advantage as a leading hydraulic hose supplier.
Evergood quality assurance system begins with the most fundamental step: raw material screening. Every batch of synthetic rubber, high-tensile steel wire, and textile fiber that enters our factory must undergo strict chemical composition analysis and physical performance testing to ensure it fully meets the highest industry standards. We know that only the best raw materials can lay a solid foundation for manufacturing an outstanding hydraulic hose.
During the production process monitoring, we use advanced automated equipment and precise process control to ensure every step is flawless. Whether it's the extrusion of the inner tube, the angle of the reinforcement layer's braid or spiral wrap, or the vulcanization of the outer cover, every step is monitored in real-time. Our technical team continuously performs in-process inspections to prevent any potential defects from moving to the next stage.
Finally, all finished products must pass a series of pre-shipment performance tests, which serve as the ultimate test for the hydraulic hose. These include:
- Pressure Test: Applying static hydrostatic pressure several times the rated working pressure to verify the hose's structural integrity and ensure no deformation or leakage occurs under high pressure.
- Pulse Test: Simulating high-frequency pressure cycles in the system to evaluate the hydraulic hose's fatigue resistance. This test is a key indicator of its long-term reliability in actual dynamic applications.
- Abrasion Test: Simulating friction in a rugged environment under controlled conditions to verify the outer cover's abrasion resistance.
- Minimum Bend Radius Test: Ensuring the hose can maintain its function under extreme bending conditions without internal structural damage or flow obstruction.
It is through this series of systematic and rigorous controls that we guarantee every Evergood hydraulic hose possesses outstanding durability, stability, and safety. Our commitment is not just to provide a product but to offer peace of mind for your operations, reducing downtime and maintenance costs caused by hose failures.
If you have any hydraulic hose procurement needs or would like to learn more about our high-performance hydraulic hose, please feel free to contact us. We look forward to working with you.
Leave a comment
Comments
-
great hydraulic hose blog
By: Edmundo On 01/23/2026This hydraulic hose blog is a practical, informative overview from design basics to real-world applications, explaining what hydraulic hoses are, how they’re built and where to use them—great for professionals choosing the right hoses.
-
hydraulic hose
By: Daza On 01/23/2026This blog on hydraulic hose is a clear, practical guide covering what hydraulic hoses are, how they’re built, where they’re used, and how to choose the right one for different applications—very helpful for both beginners and industry buyers.

















Latest comments