This air hose buying guide explores essential pneumatic hose materials (Poly, Rubber,Hybrid, PVC), diameters, and...
NPSM vs NPT Thread Hose Fittings : Key Differences and Best Uses
Introduction: Why Thread Selection Matters
Thread connections are often overlooked, yet improper selection is a major cause of industrial failure. Industry reports indicate that 15-20% of hydraulic system failures stem from connection leaks, not component defects. Understanding the difference between NPSM and NPT threads is critical for system reliability, reduced downtime, and safety.
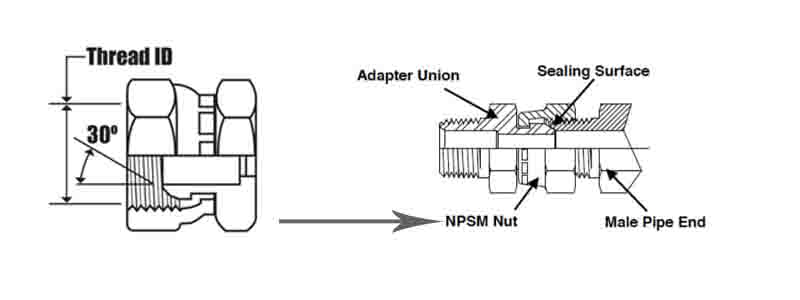
I. Understanding NPSM Thread Fitting: Straight and Mechanically Sealed
NPSM stands for National Pipe Straight Mechanical threads.
| Component | Meaning | Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| National | ANSI Standardized | American Standard Threads |
| Pipe | Fluid Transfer | Designed for piping systems |
| Straight | Defining Feature | Perfectly Parallel Diameter |
| Mechanical | Design Philosophy | Provides strength, not inherent sealing |
The core idea is that NPSM provides a strong mechanical engagement, but relies entirely on an external elastomeric seal (like an O-ring or gasket) to prevent fluid leakage.
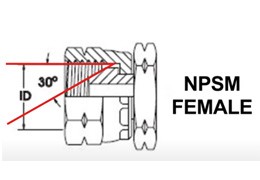
| NPSM THREAD SIZE | DASH SIZE | FEMALE THREAD ID | |
|---|---|---|---|
| (inch-TPI) | mm | inch | |
| 1/8 – 27 | -02 | 8,6 | 0.34 |
| 1/4 – 18 | -04 | 11,9 | 0.47 |
| 3/8 – 18 | -06 | 15,0 | 0.59 |
| 1/2 – 14 | -08 | 19,1 | 0.75 |
| 3/4 – 14 | -12 | 24,6 | 0.97 |
| 1 – 11.1/2 | -16 | 30,5 | 1.20 |
| 1.1/4 – 11.1/2 | -20 | 39,4 | 1.55 |
| 1.1/2 – 11.1/2 | -24 | 45,5 | 1.79 |
| 2 – 11.1/2 | -32 | 57,4 | 2.26 |
| 2.1/2 – 8 | -40 | 68,8 | 2.71 |
| 3 – 8 | -48 | 84,6 | 3.33 |
Key Characteristics
- Straight, Parallel Design: Maintains uniform thread engagement, allowing for repeated assembly and disassembly without degrading the threads.
- External Sealing Requirement: Sealing is achieved by compressing an O-ring (e.g., Nitrile, EPDM, Viton) against a seating surface.
- Matched Dimensions: Shares the same nominal diameter and thread pitch as NPT threads, but the internal geometry and function are fundamentally different.
Applications of NPSM Thread Fitting
| Application Area | Why NPSM Excels |
| Hydraulic Systems | Handles extreme pressure (>5,000PSI). Reusable design is essential for systems requiring regular servicing and component replacement. |
| Pneumatic Systems | Allows for fast, straightforward assembly without thread sealants. Provides instant, reliable sealing for air tools and automation. |
| Automotive Industry | Used in critical fuel, brake, and transmission lines where consistent, reliable performance under temperature cycling is paramount. |
Advantages & Limitations
| Advantages of NPSM | Limitations of NPSM |
| ✅ Easy Installation: No thread sealant required, translating to faster assembly. | ❌ Absolute Seal Dependency: Failure to install or using the wrong O-ring guarantees a leak. |
| ✅ High Reusability: Fittings can be reused dozens of times by simply replacing the seal. | ❌ Environmental Sensitivity: Elastomeric seals are susceptible to degradation from extreme heat, cold (e.g., below -40℃), or aggressive chemicals. |
| ✅ Seal Flexibility: Seal material (O-ring) can be customized based on fluid compatibility (e.g., Viton for aggressive solvents). | ❌ Maintenance Burden: Requires periodic inspection and proactive O-ring replacement (preventive maintenance). |
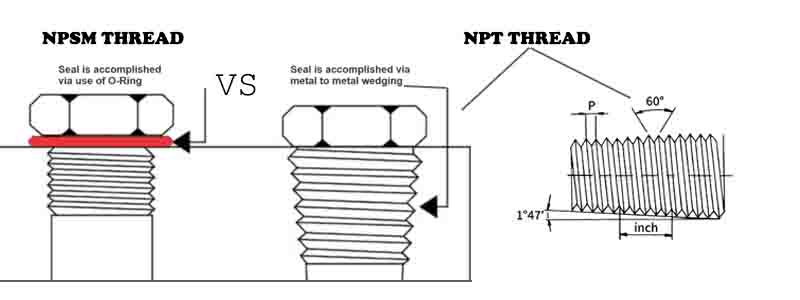
II. Understanding NPT Thread Fitting: The Tapered Alternative
External NPT stands for National Pipe Tapered threads.
Core Principle: NPT is designed on the philosophy that the seal comes from the threads themselves.
| NPT THREAD SIZE & PITCH (inch – TPI) | DASH SIZE | MALE THREAD MINOR OD | FEMALE THREAD ID | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mm | inch | mm | inch | ||
| 1/8 – 27 | -02 | 9,9 | 0.39 | 8,4 | 0.33 |
| 1/4 – 18 | -04 | 13,2 | 0.52 | 11,2 | 0.44 |
| 3/8 – 18 | -06 | 16,6 | 0.65 | 14,7 | 0.58 |
| 1/2 – 14 | -08 | 20,6 | 0.81 | 17,8 | 0.70 |
| 3/4 – 14 | -12 | 26,0 | 1.02 | 23,4 | 0.92 |
| 1 – 11.1/2 | -16 | 32,5 | 1.28 | 29,5 | 1.16 |
| 1.1/4 – 11.1/2 | -20 | 41,2 | 1.62 | 38,1 | 1.50 |
| 1.1/2 – 11.1/2 | -24 | 47,3 | 1.86 | 43,9 | 1.73 |
| 2 – 11.1/2 | -32 | 59,3 | 2.33 | 56,4 | 2.22 |
| 2.1/2 – 8 | -40 | 71,5 | 2.82 | 69,1 | 2.72 |
| 3 – 8 | -48 | 87,3 | 3.44 | 84,8 | 3.34 |
The Mechanics of Sealing
NPT threads have a consistent taper angle of 1°47'24" (approximately 1.79°). This taper results in a 1/16-inch diameter change over one inch of thread length.
When an NPT male fitting is screwed into a female counterpart, the tapered threads gradually wedge deeper, causing the thread material to slightly deform and compress against the mating threads. This physical interference creates the primary seal.
Key Characteristics of NPT Design
- Tapered Thread Geometry: Creates an increasingly tight interference fit as the fitting is tightened.
- Thread Sealant as Essential Component: NPT requires a thread sealant (PTFE tape or pipe dope) to fill the microscopic leak paths (helical gaps) left by minor imperfections in the thread geometry.
- Self-Locking Action: The wedging effect creates a self-locking connection that resists loosening from vibration or thermal cycling.
Applications Where NPT Dominates
| Application Area | Why NPT Excels |
|---|---|
| Oil and Gas Industry | The default standard for pipelines, downhole, and surface equipment due to its self-locking nature and reliability in harsh, high-pressure environments. |
| Water Supply & Plumbing | Dominant in municipal, commercial, and residential plumbing due to its simplicity, widespread availability, and cost-effectiveness. |
| HVAC Systems | Used for long-term, low-maintenance connections for water, gas, and refrigerant lines. |
Advantages & Limitation
| Advantages of NPT | Limitations of NPT |
|---|---|
| Proven Performance: Standardized since 1919, with a century of field experience and refined installation practices. | Low Reusability: Repeated assembly/disassembly wears down the thread engagement, compromising the seal. |
| Widespread & Cost-Effective: Highly standardized, readily available, and generally less expensive than equivalent NPSM fittings with seals. | Requires Sealant Management: Installation requires careful application of PTFE tape or curing pipe dope. |
| Inherent Reliability: Self-locking action provides superior resistance to vibration and thermal cycling. | Risk of Cracking: Over-tightening can cause excessive wedging, leading to thread or component cracking. |
III. Compatibility and Selection Guide
Critical Distinctions: Male vs. Female Threads
- Male Threads: External ridges (screws into a fitting).
- Female Threads: Internal grooves (the receptacle).
This distinction is crucial as sealing element placement (NPSM) and sealant application (NPT) differ based on the thread configuration.
Thread Compatibility: The Danger of Mixing
| Combination | Compatibility | Result & Warning |
| NPSM + NPSM | Compatible | Standard, reliable connection (with O-ring). |
| NPT + NPT | Fully Compatible | Standard industrial practice (with sealant). |
| NPSM + NPT | NOT RECOMMENDED | The tapered NPT thread profile works against the parallel NPSM thread, leading to thread deformation and guaranteed leaks. |
| NPTF + NPT | Compatible with Caution | Dimensionally interchangeable, but always use sealant for reliability, as NPTF tolerances are tighter. |
Selecting the Right Thread: Key Questions
| Question | If the Answer is… | Choose… |
|---|---|---|
| Maintenance Frequency? | Frequent disconnection and servicing required. | NPSM (Reusable, easy to service). |
| Permanent or long-term, fixed system. | NPT (Simple, durable, low maintenance). | |
| Pressure Range? | Below 1,000 PSI with service needs. | NPSM |
| Above 3,000 PSI sustained or high-reliability permanent connections. | NPT or specialized fittings. | |
| Fluid / Environment? | Aggressive fluids or extreme temperatures (requiring specific seal material). | NPSM (Seal flexibility). |
| Moderate environment, risk of vibration / thermal cycling. | NPT (Inherent self-locking). |
IV. Installation Best Practices
For NPSM Threads (The O-Ring Seal)
- Always use a fresh O-ring; never reuse old seals.
- Verify the O-ring material (e.g., Nitrile, Viton) is compatible with the system fluid.
- Do not over-tighten. Tighten until the O-ring is compressed and seals, then apply the specified final torque.
- Follow the regular maintenance schedule for seal inspection and replacement.
For NPT Threads (The Tapered Seal)
- Apply thread sealant (PTFE tape or pipe dope) to male threads only.
- Wrap PTFE tape clockwise (3–4 wraps).
- Tighten firmly (typically hand-tight plus 1–2 additional wrench turns) to ensure adequate thread deformation.
- Allow pipe dope to cure before pressurizing (often 24 hours).
Common Installation Mistakes to Avoid
- Cross-threading: Always start threading by hand to ensure proper alignment.
- Over-tightening: Damages threads and can crack components, leading to leaks.
- Mismatched Seals: Using the wrong O-ring material in NPSM connections.
- Wrong Sealant: Using Teflon tape when liquid pipe dope is specified, or using nothing at all on NPT.
Conclusion
NPSM and NPT threads offer two fundamentally different, yet equally valid, approaches to creating leak-free connections. While NPSM is the champion of reusability and flexibility through its external seal, NPT provides cost-efficiency and long-term reliability with its self-sealing tapered design. Choosing the right one is critical to your system's performance. Unsure which fitting is right for your equipment? Contact Evergood engineers for a free selection consultation.
Leave a comment
Comments
-
Thread Hose Fittings
By: Bonita On 01/20/2026Finally, a clear comparison! Identifying the correct thread type is crucial for safety, and this article makes it simple. Thanks to Evergood’s detailed breakdown, I purchased the perfect NPSM fittings for my industrial hoses. Excellent resource for anyone in the fluid power industry!
-
NPSM vs NPT Thread Hose Fittings
By: Deniel On 01/12/2026This guide provides a crystal-clear explanation of the critical differences between NPT and NPSM threads. The technical breakdown of tapered versus straight sealing is incredibly helpful for ensuring leak-free connections in hydraulic systems. It’s an essential resource for anyone looking to avoid costly fitting mistakes and improve system reliability!












Latest comments