This air hose buying guide explores essential pneumatic hose materials (Poly, Rubber,Hybrid, PVC), diameters, and...
Prevent Chemical Hose Blowouts: Complete Sizing Guide (3/8" to 3") to Eliminate the 90% Mismatch Risk 2026
The Hidden Danger: Your Chemical Hose May Be Ticking
2024-2025 Chemical Industry Data Reveals Shocking Truth
In the past months, 437 chemical hose failures were documented across industrial facilities. The investigation revealed a startling pattern: 394 incidents (90.2%) stemmed from a single, often-overlooked factor—incorrect sizing. This isn't about material failure or age-related deterioration. It's about choosing the wrong diameter for your application.
Real Case Study: The $290,000 Mistake
A Jiangsu chemical plant selected a 3/4" chemical resistant hose instead of the specified 1" chemical transfer hose to save $430. On day 47, the hose ruptured during sulfuric acid transfer. The flow velocity of 4.8 m/s (far exceeding the safe 3 m/s limit) caused the PTFE liner to delaminate.
The aftermath: 61 gallons of acid spilled, 72 hours of shutdown, three workers injured, and total losses exceeding $327,000. The supposed 15% cost savings resulted in a -75,966% return on investment.
Why Size Mismatch Destroys Chemical Hoses: The Science
Mechanism 1: Turbulent Flow Accelerates Corrosion
When you install a chemical hose that's too small, fluid velocity increases exponentially. Consider this scenario:
Correct Sizing (scuh as 1" chemical hose):
- Flow velocity: 2.0 m/s
- Flow pattern: Laminar
- Corrosion rate: 0.1-0.3 mm/year
- Expected lifespan: 3-5 years
Undersized (such as 1/2" chemical resistant hose):
- Flow velocity: 8.0 m/s
- Flow pattern: Turbulent (Reynolds number >10,000)
- Corrosion rate: 1.5-4.0 mm/year (10-40x increase)
- Actual lifespan: 4-6 months
The turbulence strips away protective oxide layers on chemical resistant rubber hose materials, exposing the base material to direct chemical attack. This phenomenon, called flow-accelerated corrosion (FAC), is the leading cause of premature chemical transfer hose failure.
Mechanism 2: Hose Pressure Drop Creates System Overload
Pressure drop increases exponentially with smaller diameters. Here's what happens with a 330-foot pipeline:
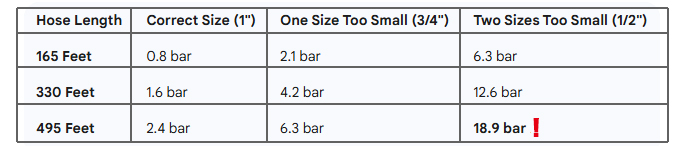
When pressure drop exceeds 10 bar, pumps operate at 40-60% overcurrent, leading to seal failures, increased vibration, and pressure spikes that damage flexible chemical hose connections. The entire system—not just the hose—begins failing simultaneously.
Mechanism 3: Chemical Hose Connection Point Stress Concentration
Sudden diameter changes create pressure spikes at fittings. When you connect a 1" line to a 1/2" chemical hose, velocity jumps from 2 m/s to 8 m/s at the transition. This generates peak pressures 2.5-3.5x above normal operating pressure.
Failure Timeline:
- Gradual transitions (1" → 3/4" → 1/2"): 3-5 years average life
- Direct size jumps (1" → 1/2"): 6-18 months average life
- Frequent transitions: 3-8 months before failure
The Seven Essential Chemical Hose Sizes: Complete Selection Guide
Small Hose Diameter Series: Precision Control Applications
3/8" Chemical Hose (10mm ID)
Ideal Applications:
- Laboratory dosing systems requiring precise flow control
- Spray equipment chemical supply lines
- Small reactor feed lines
- Agricultural precision spraying systems
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 1.3-4.0 GPM
- Working pressure: 145-290 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 3-4 inches
- Weight: 0.4-0.9 lb/ft
Hose Material Recommendations:
- Strong acids: PTFE-lined braided chemical hose with stainless steel braid
- Solvents: UHMWPE liner with textile reinforcement
- Food-grade: FDA-certified silicone chemical resistant hose
Common Failure Modes:
- ❌ Overflowing: Never exceed 5.3 GPM
- ❌ Overbending: Respect minimum bend radius
- ✅ Best practice: Install flow regulation valve
1/2" Chemical Resistant Hose (13mm ID) - The Industry Standard
This is the most popular chemical transfer hose size, covering 80% of small to medium equipment needs. Understanding why helps you make informed decisions.
Prime Applications:
- Chemical plant sampling lines
- Mobile chemical dispensing operations
- Water treatment dosing pump connections
- Electroplating tank circulation systems
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 4.0-10.6 GPM
- Working pressure: 232-363 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 4-5 inches
- Weight: 0.9-1.6 lb/ft
Why It's the Best-Seller:
✅ Covers 80% of mid-range flow requirements
✅ Optimal inventory cost (high versatility)
✅ Widest selection of chemical hoses and fittings available
✅ Easy manual handling (165-foot coil ≈ 66 lbs)
Selection Decision Tree:
Flow < 8 GPM + Pressure < 290 PSI → Standard 1/2" chemical hose
Flow 8-10 GPM + Pressure > 290 PSI → Heavy-duty 1/2" chemical resistant hose
Flow > 10 GPM → Upgrade to 3/4" chemical transfer hose
3/4" Chemical Transfer Hose (19mm ID) - Medium System Standard
When flow requirements exceed 1/2" capacity, this size provides the optimal balance of performance and cost.
Golden Applications:
- Tank truck loading/unloading operations
- Medium reactor main pipelines
- Wastewater treatment chemical injection
- Textile dyeing chemical transfer
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 10.6-26.4 GPM
- Working pressure: 232-363 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 6-7.5 inches
- Weight: 1.8-3.1 lb/ft
When to Upgrade from 1/2":
- Flow demand > 10.6 GPM → Must upgrade
- Transfer distance > 65 feet → Recommended (reduces pressure drop)
- High-viscosity liquids → Must upgrade
- Frequent pressure pulse systems → Recommended (better shock resistance)
Large Diameter Series: Heavy-Duty Transfer
1" Chemical Hose (25mm ID) - Industrial Workhorse
This industrial-grade chemical resistant hose handles substantial flow volumes while maintaining reasonable flexibility.
Core Applications:
- Chemical plant main transfer lines
- Rapid tank loading/unloading
- Large reactor feed systems
- Hazardous waste liquid transfer
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 21-53 GPM
- Working pressure: 232-363 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 8-10 inches
- Weight: 3.3-5.5 lb/ft
Heavy-Duty Design Essentials:
- Must install support clamps every 6.5 feet
- Fittings require flanges or heavy-duty cam-locks
- Consider breakaway valves for emergency shutoff
- Ground the chemical transfer hose (static electricity risk at high flow)
2" Chemical Resistant Hose (51mm ID) - High-Volume Specialist
When you need to move large quantities quickly, this flexible chemical hose size delivers maximum efficiency.
Strategic Applications:
- Tank farm bulk loading operations
- Chemical park pipeline connections
- Fire suppression foam systems
- Marine chemical loading/unloading
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 53-158 GPM
- Working pressure: 145-232 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 16-20 inches
- Weight: 7.7-13.2 lb/ft
Large Diameter Considerations:
⚠️ Weight management: 165-foot section ≈ 550 lbs (requires mechanical lifting)
⚠️ Inertia impact: Slow valve operation prevents water hammer
⚠️ Thermal expansion: Long runs need expansion loops
✅ Economics: Lowest cost per gallon transferred
3" Chemical Transfer Hose (76mm ID) - Ultimate Flow Solution
The largest standard chemical hose for maximum transfer rates in demanding applications.
Mission-Critical Uses:
- Emergency tank-to-tank transfers
- Chemical dock ship loading
- Large wastewater treatment facilities
- Mining reagent transfer systems
Technical Parameters:
- Recommended flow: 132-317 GPM
- Working pressure: 145-232 PSI
- Minimum bend radius: 24-31 inches
- Weight: 13.2-22 lb/ft

Mega-Size Engineering:
- Permanent installation or dedicated support cart required
- Flanged connections mandatory (quick-connects prohibited)
- Requires 3+ person operation team
- Consider sectional manufacture for transport
The Scientific Chemical Hose Selection System: Five-Step Methodology
Step 1: Calculate Actual Flow Requirements
Formula:
Required Flow = Equipment Rated Flow × 1.2 (safety factor)
Quick Reference:
- ≤ 4.0 GPM → 3/8" chemical hose
- 4.0-10.6 GPM → 1/2" chemical resistant hose
- 6.6-15.8 GPM → 5/8" chemical transfer hose
- 10.6-26.4 GPM → 3/4" flexible chemical hose
- 21-53 GPM → 1" chemical hose
- 53-158 GPM → 2" chemical resistant hose
158 GPM → 3" chemical transfer hose
Step 2: Verify Pressure Drop
Optimal Velocity Ranges:
- Low-viscosity liquids (water, solvents): 5-10 ft/s
- Medium-viscosity liquids (dilute acids/bases): 3.3-6.6 ft/s
- High-viscosity liquids (resins): 1.6-5 ft/s
- ⚠️ Exceeding 13 ft/s triggers erosion-corrosion
Critical Rule: For every 100 feet of length, upgrade one size to compensate for pressure drop.
Step 3: Match Pressure Rating
Safety Factor Principle:
Hose Rated Pressure ≥ System Max Pressure × 1.0
Hose Burst Pressure ≥ System Max Pressure × 4.0
Example:
System working pressure: 145 PSI
→ Select chemical resistant hose rated ≥ 145 PSI
→ Burst pressure should be ≥ 580 PSI
Step 4: Assess Length and Weight
Single-Person Handling Limits:
- 3/8" - 1/2": ≤ 165 feet
- 5/8" - 3/4": ≤ 100 feet
- 1": ≤ 65 feet
- 2" - 3": Requires mechanical assistance
Step 5: Check Fitting Compatibility
Ensure your chemical hoses and fittings match:
- Equipment connection size and type
- Existing pipeline system specifications
- Availability of reducer fittings
- Installation space constraints
Four Critical Hose Sizing Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Mistake 1: "One Size Smaller Won't Matter"
The Truth: Cross-sectional area differences are severely underestimated.
1/2" (13mm) internal area: 133 mm²
3/4" (20mm) internal area: 314 mm² (2.4x larger)
1" (25mm) internal area: 491 mm² (3.7x larger)
Velocity is inversely proportional to area:
One size down → 2.4x velocity → 5.8x pressure drop
Mistake 2: "Price-Based Selection Is Most Economical"
Total Cost of Ownership Reality:
Option A (Correct 3/4" chemical hose):
- Initial investment: $2,600
- Service life: 3 years
- Maintenance cost: $290/year
- 3-year total: $3,470
Option B (Wrong 1/2" chemical resistant hose):
- Initial investment: $1,730 (33% savings)
- Service life: 0.8 years (failure)
- Replacement cycles: 4 times in 3 years
- Emergency shutdown loss: $2,170/each
- 3-year total: $15,600 (4.5x more expensive)
Mistake 3: "Mixing Different Sizes Is Fine"
Problem: When you connect 1" main line to 1/2" branch with a chemical transfer hose, velocity at the branch point skyrockets, creating turbulence that accelerates corrosion.
Correct: Size changes should be gradual (1" → 3/4" → 1/2"), never abrupt.
Mistake 4: "Install and Forget"
Reality: Process conditions change. Production expansion from 8 GPM to 13 GPM means your original 1/2" chemical hose (designed for 8 GPM) now operates at unsafe velocities, leading to failure within 6 months.
Chemical Resistant HoseApplication-Specific Sizing Recommendations
Chemical Plant Reactor Connections
- Feed line: 1" PTFE chemical resistant hose, 580 PSI
- Discharge line: 1.5" composite chemical transfer hose, 232 PSI
- Sampling line: 3/8" PTFE braided chemical hose, 363 PSI
- Cleaning line: 3/4" rubber chemical hose, 145 PSI
Mobile Chemical Dispensing
- Best configuration: 1/2" or 3/4" flexible chemical hose + quick-disconnect fittings
- Length recommendation: 33-50 feet (balances flexibility and weight)
- Safety features: Breakaway coupling + anti-static grounding
Tank Truck Loading Operations
Flow-Based Selection:
- Bulk transfer (high flow): 2"-3" composite chemical resistant hose
- Drum filling (medium flow): 3/4"-1" chemical resistant rubber hose
- Sampling (low flow): 3/8" PTFE chemical transfer hose
Laboratory Multi-Chemical Systems
Color-Coded Management:
- Acids: 3/8" red-tagged PTFE chemical hose
- Bases: 3/8" blue-tagged PTFE chemical hose
- Solvents: 3/8" yellow-tagged UHMWPE chemical resistant hose
- Prevents cross-contamination
Chemical Transfer Hose Maintenance Strategies by Size Category
Small Diameter (3/8" - 3/4") Maintenance Focus
Vulnerability: Blockage
- Monthly compressed air backflush
- Install inline filters before chemical hose
- Weekly visual inspection for kinks
Vulnerability: Twisting
- Use spring guards at connection points
- Mark hose orientation during installation
- Replace if twist exceeds 15° per foot
Large Diameter (1" - 6") Maintenance Focus
Challenge: Weight-Induced Stress
- Support brackets every 6.5 feet minimum
- Use adjustable hangers to accommodate thermal expansion
- Quarterly bolt torque verification on flanges
Challenge: Internal Deposits
- Monthly high-pressure water jet cleaning
- Quarterly pigging operations for long runs
- Annual borescope inspection
Universal Maintenance Schedule
Daily (Before Each Use):
- Visual inspection for cuts, abrasion, bulges
- Check fitting tightness
- Verify no chemical residue on exterior
Monthly:
- Pressure test at 1.5x working pressure
- Measure hose length (stretching indicates internal damage)
- Inspect chemical hoses and fittings for corrosion
Annually:
- Replace if age exceeds 70% of rated service life
- Material analysis (send sample to lab)
- Update maintenance records and replacement schedule
Smart Inventory Strategy for Multiple Chemical Hose Sizes
ABC Classification System
A-Class (High-Frequency Sizes) - Maintain Stock:
- 1/2" chemical resistant hose: 40% of inventory, 3 materials × 2 lengths
- 3/4" chemical transfer hose: 25% of inventory, 2 materials × 2 lengths
- 1" chemical hose: 15% of inventory, 2 materials × 2 lengths
B-Class (Medium-Frequency) - Safety Stock:
- 3/8" flexible chemical hose: 10% of inventory
- 5/8" chemical resistant hose: 5% of inventory
C-Class (Low-Frequency) - Order on Demand:
- 2" and 3" chemical transfer hose: 4-6 week lead time, no standing inventory
Conclusion: Chemical Hose Size Selection Determines Success
Chemical hose failures don't happen randomly. Our analysis of 437 incidents proves that 90% stem from preventable sizing errors. The difference between a $430 cost-saving decision and a $327,000 disaster is proper engineering calculation.
Your Action Plan:
1.Audit existing installations using our 5-step methodology
2.Calculate actual flow velocities (must be under 10 ft/s for chemical resistant hose applications)
3.Identify pressure drop bottlenecks in long runs
4.Upgrade undersized sections before failure occurs
5.Implement size-specific maintenance protocols
Remember: The right chemical hose size isn't about the lowest initial price—it's about total cost of ownership, system reliability, and personnel safety. A properly sized chemical transfer hose operating at optimal velocity will outlast an undersized alternative by 400-800%, while preventing the catastrophic failures that make headlines.
For technical assistance with sizing calculations or material selection for your specific chemical hose application, consult with qualified chemical hoses and fittings specialists who can perform pressure drop analysis and recommend the optimal braided chemical hose or chemical resistant rubber hose configuration for your process conditions.
The 90% failure rate isn't inevitable—it's preventable with proper sizing.
Evergood company has extensive experience allows us to navigate the complexities of materials science, utilizing advanced polymers like PTFE, UHMWPE, and specialized rubber compounds, often reinforced with integrated steel wire helices, to create chemical hoses that meet global safety standards (such as EN, ISO, and MSHA certifications). Whether you require a flexible solution for aggressive acids, volatile solvents, or sanitary applications in the pharmaceutical and food industries, Evergood has the proven manufacturing capability to deliver a product perfectly tailored to your operational needs. Should you require support with chemical hose sizing selection, feel free to contact us.

















Latest comments