This air hose buying guide explores essential pneumatic hose materials (Poly, Rubber,Hybrid, PVC), diameters, and...
Mastering Hydraulic Hose Fabrication-A Professional Engineering Approach
Hydraulic Hose Fabrication Introduction
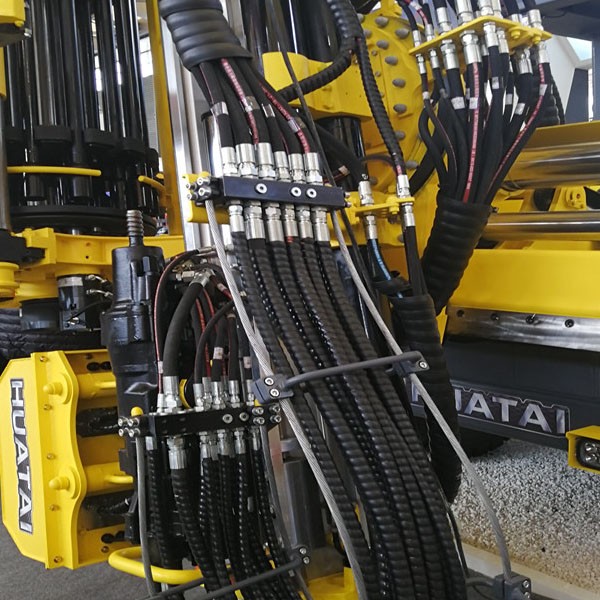
Hydraulic systems power industrial equipment through controlled pressurized fluid flow, with hoses serving as vital transmission arteries. The quality of hydraulic hose fabrication cannot be overstated in its importance for both safety and operational efficiency. A poorly fabricated hose can lead to catastrophic system failures, costly downtime, environmental contamination, and potentially life-threatening accidents. Conversely, proper hydraulic hose fabrication techniques ensure optimal performance, extended service life, and reliable operation under demanding conditions.
This comprehensive guide presents an engineering-focused methodology for mastering the art and science of hydraulic hose fabrication. Our approach centers on advanced material science principles and meticulous handling of flexible hose pipe components, providing you with the knowledge and techniques necessary to create hydraulic assemblies that meet the highest standards of quality and safety through expert hydraulic hose fabrication. Understanding the proper characteristics of each flexible hose pipe is essential for successful system implementation.
Chapter 1: Advanced Material Engineering and Compatibility Analysis on hydraulic hose fabrication
The foundation of successful hydraulic hose fabrication begins with comprehensive material analysis, extending far beyond basic material selection to include molecular-level compatibility studies and long-term degradation modeling. This engineering approach considers not only immediate performance requirements but also projected service life under varying operational stresses.
Modern synthetic rubber compounds represent sophisticated polymer matrices designed for specific hydraulic applications. Nitrile rubber (NBR) with varying acrylonitrile content provides tailored resistance to petroleum-based fluids, with higher acrylonitrile percentages offering superior chemical resistance at the expense of low-temperature flexibility. Advanced formulations incorporate carbon black reinforcement and antioxidant packages that significantly extend service life in demanding applications.
Thermoplastic elastomers have revolutionized flexible hose pipe design through their unique combination of processing advantages and performance characteristics. Polyurethane-based systems offer exceptional abrasion resistance and maintain structural integrity through millions of flex cycles, making them ideal for mobile hydraulic applications where dynamic movement is constant. These materials exhibit superior tear strength and cut resistance compared to traditional rubber compounds.
Metal hose construction utilizing stainless steel provides unparalleled chemical compatibility and temperature resistance. Corrugated metal flexible hose pipe designs accommodate thermal expansion while maintaining pressure integrity across extreme temperature ranges. The critical aspect of material selection lies in matching the flexible hose pipe material properties to both the hydraulic fluid characteristics and the operating environment through detailed compatibility matrices and accelerated aging tests.
Chapter 2: Flexible Hose Pipe-Reinforcement Architecture and Stress Distribution Engineering
The reinforcement layer transforms a basic flexible hose pipe into an engineered pressure vessel capable of withstanding extreme forces while maintaining precise dimensional control under pressure. This transformation involves complex stress distribution analysis and multi-layer reinforcement strategies that optimize both strength and flexibility characteristics.
Advanced braiding techniques employ mathematical models to determine optimal wire angles and crossing patterns for maximum hose strength. Single-wire braided constructions typically utilize crossing angles between 54-60 degrees to achieve optimal hoop stress distribution, while double-wire braided systems employ alternating layer angles to create balanced circumferential and longitudinal strength. The braiding tension and wire pre-stress significantly impact the final pressure rating and fatigue life of the flexible hose pipe structure.
Spiral-wrapped reinforcement systems offer advantages in high-pressure applications where maximum strength-to-weight ratios are critical. These constructions utilize continuous wire wrapping at precise angles calculated to resist internal pressure while accommodating bending stresses. The spiral pitch and wire tension must be carefully controlled to prevent wire migration and maintain consistent pressure ratings throughout the flexible hose pipe length.
Textile reinforcement systems utilize high-strength synthetic fibers arranged in complex braiding patterns optimized for specific loading conditions. Aramid fiber reinforcement provides exceptional tensile strength with minimal weight penalty, while polyester systems offer cost-effective performance for moderate pressure applications. The selection between steel wire and textile braiding depends on the specific flexible hose pipe application requirements, with consideration given to fatigue life, environmental exposure, and system weight constraints.
Chapter 3: Hydraulic Hose Assembly-Precision Metrology and Advanced Cutting Methodologies
Professional hydraulic hose fabrication demands metrological precision that extends beyond simple length measurement to include comprehensive geometric analysis and tolerance verification. This systematic approach ensures optimal system performance while minimizing stress concentrations that lead to premature failure.
The measurement protocol begins with detailed system analysis incorporating thermal expansion calculations, pressure-induced length changes, and dynamic movement requirements. These factors combine to determine the optimal installed length for each flexible hose pipe application. Advanced measurement techniques utilize laser measurement systems and coordinate measuring machines to achieve sub-millimeter accuracy in critical applications.
Geometric considerations include bend radius calculations, routing clearances, and interference analysis with adjacent components. Computer-aided design tools enable three-dimensional routing optimization that minimizes stress while ensuring adequate service access. The flexible hose pipe installation requirements must account for assembly tolerances, mounting variations, and operational movement ranges.
Advanced cutting technologies employ computer-controlled cutting systems that maintain precise perpendicularity while minimizing material distortion. These systems utilize diamond-coated blades or high-frequency cutting methods that create clean cuts without thermal damage to synthetic materials. The cutting parameters must be optimized for each flexible hose pipe construction to prevent delamination and ensure proper fitting installation.
Quality verification protocols include dimensional inspection using precision measuring instruments and visual examination under magnification to detect cutting defects. Any variations from specification require correction before proceeding with assembly operations.
Chapter 4: Hydraulic Fitting Integration and Sealing System Design
Hydraulic hose fitting integration represents a critical interface where mechanical engineering principles determine long-term system reliability. This process involves detailed analysis of stress concentrations, seal dynamics, and material compatibility to ensure leak-free operation throughout the hose service life.
Modern hydraulic fitting designs utilize advanced metallurgy and precision machining to create optimal sealing surfaces and stress distribution characteristics. The fitting geometry must accommodate the flexible hose pipe internal structure while providing adequate clamping force without causing material damage. Surface treatments and coatings enhance corrosion resistance and improve hose assembly characteristics.
Seal system design considers both static and dynamic sealing requirements, with elastomeric compounds selected for specific fluid compatibility and temperature resistance. O-ring groove dimensions follow precise standards to ensure proper compression and prevent extrusion under pressure. Advanced sealing systems may incorporate backup rings and specialized compounds for extreme service conditions.
The insertion process requires controlled force application to prevent flexible hose pipe damage while ensuring complete seating. Specialized insertion tools and lubrication systems facilitate proper assembly while maintaining cleanliness standards. The hydraulic fitting must be inserted to specified depths with verification through measurement or visual indicators.
Quality assurance protocols include dimensional verification, seal inspection, and assembly torque verification to ensure consistent results across all assemblies.
Chapter 5: Advanced Hydraulic Crimping Technology and Process Control
Hydraulic hose fabrication crimping represents a sophisticated manufacturing process where precise control over multiple variables determines the mechanical properties and reliability of the finished assembly. This critical operation requires understanding of material deformation mechanics, force distribution analysis, and quality control methodologies.
Modern crimping systems utilize servo-controlled hydraulic actuators with real-time force monitoring and position feedback to achieve consistent results. The hose crimping process involves complex metal flow analysis as the hydraulic fitting ferrule deforms to create the permanent mechanical bond. Finite element analysis guides the selection of crimping parameters to optimize strength while preventing material damage.
Process monitoring systems track crimping force, displacement, and hold time to ensure consistency across production runs. Statistical process control methods identify variations that could affect hose quality, enabling proactive adjustments to maintain specification compliance. Data logging systems provide complete traceability for quality assurance and failure analysis.
Die selection and maintenance play critical roles in achieving optimal crimp geometry. Precision-machined dies with specific profiles create the force distribution patterns necessary for reliable joints. Regular inspection and replacement of worn dies prevents dimensional variations that compromise assembly quality.
The importance of correct crimp diameter cannot be overstated, as this dimension directly affects both the mechanical strength and sealing capability of the hose assembly. Under-crimping results in inadequate retention force and potential fitting blow-off under pressure, while over-crimping can damage the flexible hose pipe reinforcement and create stress concentration points that lead to premature failure through professional hydraulic hose fabrication methods.
Chapter 6: Flexible Hose Pipe-Comprehensive Testing Protocols and Quality Validation
Advanced testing methodologies provide comprehensive validation of hydraulic hose fabrication quality through systematic evaluation of mechanical properties, seal integrity, and long-term performance characteristics. These protocols extend far beyond basic pressure testing to include fatigue analysis, environmental testing, and failure mode evaluation.
Pressure testing protocols follow established industry standards while incorporating enhanced safety measures and data acquisition systems. Test pressures typically exceed working pressure by specified safety factors, with careful monitoring of pressure decay rates that indicate seal performance. Advanced testing systems provide real-time pressure measurement with data logging capabilities for quality documentation.
Fatigue testing evaluates flexible hose pipe performance under cyclic loading conditions that simulate actual service environments. These tests involve repeated pressure cycling, bending cycles, and environmental exposure to predict service life under various operating conditions. Accelerated testing protocols compress years of service into weeks of testing time through elevated stress levels and environmental conditions.
Burst testing determines ultimate strength characteristics and failure modes under extreme conditions. These destructive tests provide valuable data for safety factor calculations and design validation. High-speed photography and instrumentation capture failure mechanisms for analysis and design improvement.
Environmental testing exposes hose pipe assemblies to temperature extremes, chemical exposure, and accelerated aging conditions to evaluate long-term performance. These tests identify potential degradation mechanisms and validate material selection decisions for specific applications.
Chapter 7: Professional Hydraulic Hose Installation Engineering and System Integration
Professional installation practices ensure that precision-fabricated hydraulic hose assemblies achieve optimal performance through proper system integration and protection measures. This engineering approach considers system dynamics, environmental factors, and maintenance requirements to maximize service life and reliability.
Routing analysis utilizes three-dimensional modeling to optimize flexible hose pipe paths while minimizing stress concentrations and interference with system components. Computer simulation tools predict system behavior under various operating conditions, enabling proactive design modifications to prevent problems. The route should minimize the number of bends while maintaining adequate clearance from moving parts, sharp edges, and heat sources through careful flexible hose pipe geometry planning.
Dynamic analysis considers system movement, vibration, and pressure pulsations that affect flexible hose pipe loading throughout the operating cycle. Finite element analysis tools predict stress distributions and identify potential failure locations for prevention through design modifications. The use of gradual bends rather than sharp direction changes helps distribute stress more evenly throughout the flexible hose pipe structure.
Support system design follows engineering principles to provide adequate restraint while accommodating thermal expansion and operational movement. Specialized clamps and mounting hardware distribute loads evenly to prevent stress concentrations. Support spacing calculations consider hydraulic hose specifications, pressure ratings, and dynamic loading conditions.
Environmental protection systems shield flexible hose pipe assemblies from mechanical damage, chemical exposure, and thermal stress. Advanced protective systems may include heated enclosures, chemical-resistant sleeves, and impact guards designed for specific applications. Heat protection becomes essential in applications where flexible hose pipe assemblies are exposed to elevated temperatures from engines, exhaust systems, or heated hydraulic fluid.
Conclusion-The Fabrication of Flexible Hydraulic Hose
The advanced methodology outlined in this comprehensive guide provides the engineering foundation for creating superior hydraulic assemblies that exceed conventional performance standards. Each phase, from materials engineering through system integration, contributes to the overall reliability and performance of the finished assembly through expert hydraulic hose fabrication.
Professional hydraulic hose fabrication requires understanding that each step builds upon scientific principles and engineering analysis rather than simple procedural compliance. The selection of appropriate materials ensures compatibility and longevity through detailed analysis, while advanced reinforcement provides the strength necessary for demanding applications. Precision measurement and cutting establish the foundation for proper fitting installation, and sophisticated crimping creates the permanent bond that holds everything together through professional hydraulic hose fabrication methods.
Quality validation through comprehensive testing protocols ensures that the hydraulic hose fabrication process meets the most demanding requirements, while engineered installation practices maximize service life and system reliability. Neglecting any aspect of this systematic approach can compromise the entire assembly, leading to premature failure, safety hazards, and costly system downtime.
The hydraulic industry continues advancing with new materials, manufacturing technologies, and increasingly sophisticated applications. However, the fundamental engineering principles of quality hydraulic hose fabrication remain constant: scientific analysis, precision manufacturing, and systematic quality control. By implementing these advanced methodologies and maintaining the highest technical standards throughout the hydraulic hose fabrication process, hydraulic professionals can create assemblies that provide exceptional service in the most challenging applications.
As you implement these hydraulic hose fabrication techniques in professional practice, remember that engineering excellence requires continuous learning and adaptation to new technologies and methods. The investment in proper hydraulic hose fabrication procedures and advanced quality control systems yields significant returns through enhanced reliability, reduced maintenance costs, and the confidence that comes from engineering excellence that meets the highest professional standards.If you have hydraulic pipe purchasing needs, please contact us.


















Latest comments